Ways to Integrate Digital Fabrication in Architecture
Ever wondered how architects can use advanced technology to revolutionize building design and construction? Digital fabrication in architecture involves utilizing cutting-edge tools and techniques to create complex structures with precision and efficiency. By embracing digital fabrication, architects can innovate their design processes and streamline construction workflows. Let’s explain practical ways to integrate digital fabrication in architecture.
Integrating Digital Fabrication in Architecture
3D Printing
3D printing technology enables architects to create intricate models and full-scale building components layer by layer. Architects use 3D printers to fabricate detailed architectural models, prototypes, and custom building components with precision and speed. This technology allows for rapid iteration and customization of designs, facilitating experimentation with complex geometries and innovative forms. By harnessing 3D printing, architects can reduce material waste, shorten construction timelines, and achieve greater design flexibility in architectural projects.

CNC Machining
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining involves automated tools that precisely cut and shape materials based on digital design files. Architects utilize CNC machines to fabricate architectural elements such as facades, panels, and decorative features from various materials including wood, metal, and composites. CNC machining offers high precision and repeatability in manufacturing complex forms and intricate details that would be challenging to achieve through traditional methods. Integrating CNC technology enhances architectural design capabilities and ensures accuracy in fabrication processes.
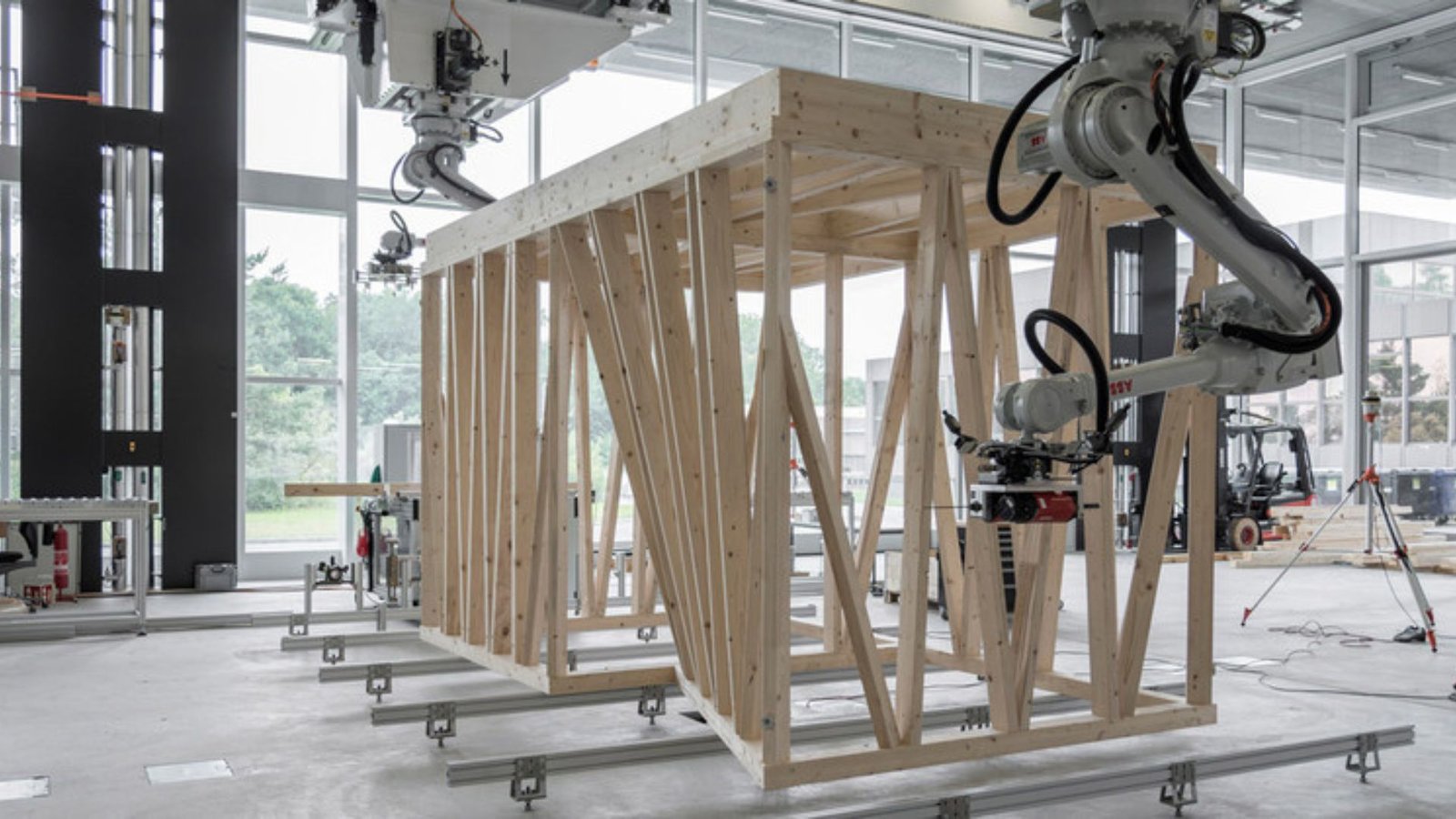
Robotic Construction
Robotic construction systems utilize robotic arms and automated machinery to assemble building components and perform construction tasks on-site. Architects deploy robotic systems for tasks such as bricklaying, concrete pouring, and prefabricated panel assembly. Robotic construction improves construction efficiency, reduces labour costs, and enhances safety on construction sites. By automating repetitive and labour-intensive tasks, architects can accelerate construction schedules and achieve higher quality standards in building assembly.
Parametric Design
Parametric design software allows architects to create and manipulate digital models based on parameters and algorithms. Architects use parametric tools to generate complex geometries and optimize designs for digital fabrication processes. Parametric design facilitates iterative design exploration and optimization of structural performance, material efficiency, and environmental considerations. By integrating parametric design principles, architects can create adaptive and responsive architectural forms that are tailored to specific project requirements and site conditions.
Digital Twins
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical buildings that integrate real-time data and simulations to monitor and optimize building performance. Architects utilize digital twins to analyze energy efficiency, occupant comfort, and operational sustainability throughout the building lifecycle. By incorporating sensor data and simulation models, architects can identify performance improvements and predictive maintenance strategies for optimized building operation. Digital twins enable architects to make informed design decisions and enhance building resilience and sustainability.
Modular Construction: Prefabricating Building Components
Modular construction involves prefabricating building components off-site in controlled factory conditions before assembling them on-site. Architects leverage modular construction techniques to fabricate modules such as wall panels, floor systems, and bathroom pods with digital fabrication technologies. Modular construction reduces construction time, minimizes site disruption, and improves construction quality by ensuring consistent manufacturing standards. By integrating digital fabrication in modular construction, architects can achieve cost-effective and sustainable building solutions tailored to project timelines and client requirements.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) technologies enable architects to visualize and experience architectural designs in immersive virtual environments. Architects use AR and VR to simulate spatial layouts, evaluate design proportions, and engage stakeholders in interactive design reviews. These technologies enhance communication, collaboration, and decision-making throughout the design and construction phases. By integrating AR and VR into design workflows, architects can enhance design visualization, client presentations, and project coordination.
Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building. Architects use BIM software to create intelligent 3D models that integrate architectural design, engineering systems, and construction information. BIM facilitates collaborative design coordination, clash detection, and construction documentation management. By leveraging BIM capabilities, architects can streamline project workflows, improve design accuracy, and optimize construction sequencing. BIM integration supports digital fabrication by providing comprehensive data for fabricating and assembling building components with precision.
Conclusion
Integrating digital fabrication technologies revolutionizes architectural design and construction practices by enhancing precision, efficiency, and design innovation. By adopting 3D printing, CNC machining, robotic construction, parametric design, digital twins, modular construction, AR/VR visualization, and BIM collaboration, architects can optimize building performance and sustainability. Embracing digital fabrication not only expands architectural possibilities but also promotes sustainable building practices and advances resilience in the built environment.