Predictions for the Future of Architecture
- By -Peter
- Posted on
- Posted in Architectural Design
The future of architecture is poised to be shaped by technological advancements, sustainability imperatives, and evolving societal needs. This article explores predictions for the future of architecture, focusing on the concepts of smart cities and adaptive reuse.
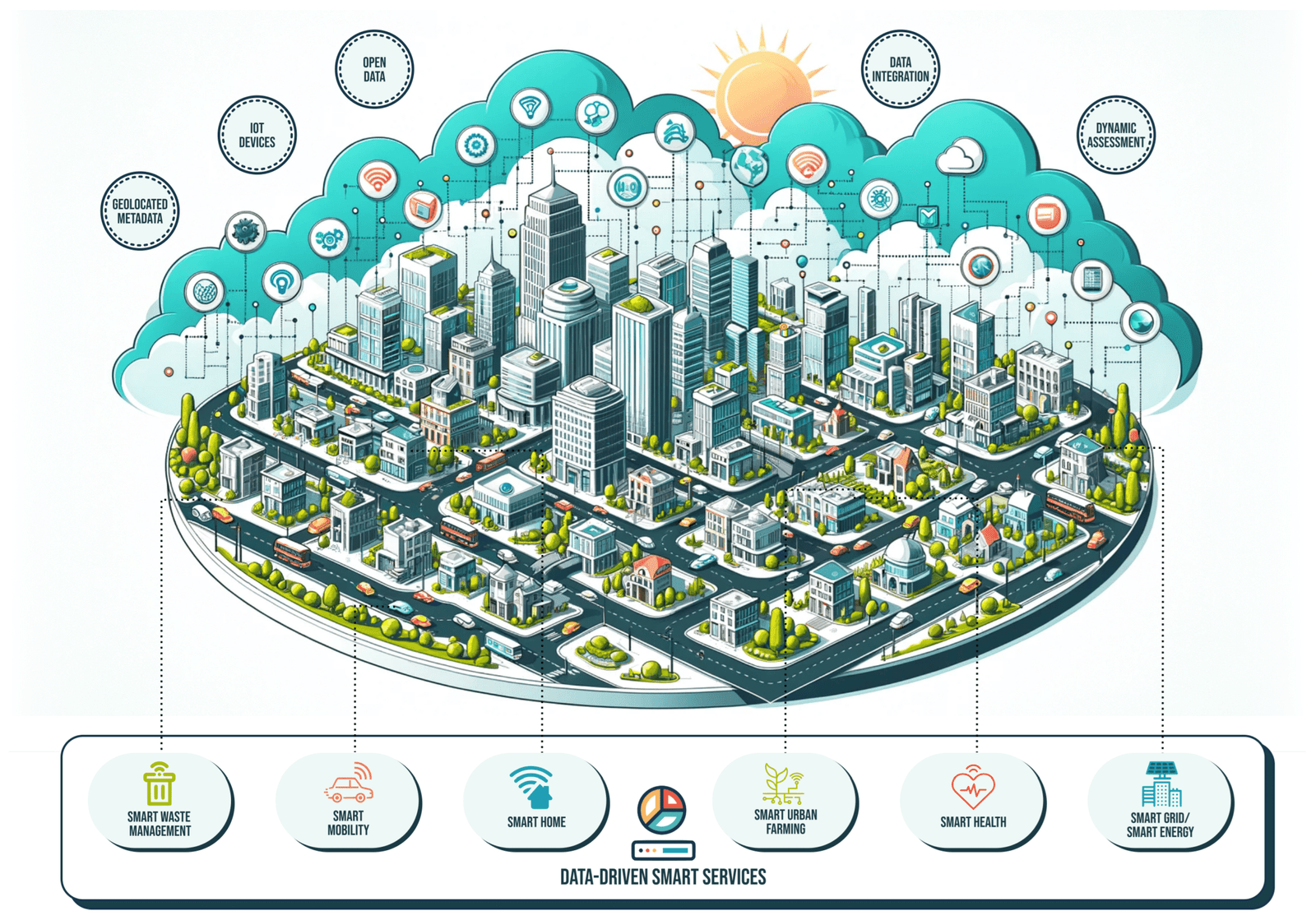
1. Smart Cities
Definition and Vision: Smart cities integrate technology and data-driven solutions to enhance urban living. These cities leverage the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and other advanced technologies to create more efficient, sustainable, and livable urban environments.
Key Predictions:
- Connected Infrastructure: Future cities will feature interconnected infrastructure where buildings, transportation systems, utilities, and public services communicate seamlessly. This integration will optimize resource use, reduce waste, and improve urban efficiency.
- Sustainable Urban Planning: Smart cities will prioritize sustainability, incorporating green spaces, renewable energy sources, and sustainable building materials. Urban planners will design cities to reduce carbon footprints, promote biodiversity, and enhance residents’ well-being.
- Intelligent Transportation Systems: Autonomous vehicles, smart traffic management, and integrated public transit systems will revolutionize urban mobility. These advancements will reduce congestion, lower emissions, and improve accessibility.
- Responsive Buildings: Buildings in smart cities will be equipped with sensors and automation systems to monitor and adapt to environmental conditions. This includes energy-efficient lighting, heating, and cooling systems that respond to occupancy and weather patterns.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Real-time data collection and analysis will inform urban planning and management. Cities will use data to anticipate and address issues such as traffic congestion, pollution, and emergency responses.
Examples and Current Trends:
- Songdo International Business District (South Korea): A planned smart city with integrated technology for energy management, waste disposal, and transportation.
- Masdar City (UAE): A sustainable urban development project aiming to become a zero-carbon, zero-waste city powered by renewable energy.
2. Adaptive Reuse
Definition and Vision: Adaptive reuse involves repurposing existing buildings for new uses, preserving cultural heritage, and reducing environmental impact. This approach addresses the growing need for sustainable development and efficient use of resources.
Key Predictions:
- Sustainable Development: Adaptive reuse will become a cornerstone of sustainable architecture, reducing the need for new construction and minimizing demolition waste. This practice will help preserve historical and culturally significant buildings while meeting modern needs.
- Flexible Spaces: Future buildings will be designed with adaptability in mind, allowing spaces to be easily reconfigured for different uses over time. This flexibility will extend the lifespan of structures and accommodate changing societal needs.
- Integration of Modern Amenities: Repurposed buildings will incorporate modern amenities and technologies while retaining their historical character. This includes upgrading energy systems, improving accessibility, and enhancing structural integrity.
- Community Revitalization: Adaptive reuse projects will play a crucial role in revitalizing urban areas, transforming underutilized or abandoned buildings into vibrant community hubs. This approach fosters economic development, cultural preservation, and social cohesion.
- Architectural Innovation: Architects will develop creative solutions to integrate old and new elements harmoniously, blending historical aesthetics with contemporary functionality.
Examples and Current Trends:
- Tate Modern (London, UK): A former power station transformed into a world-renowned art museum, preserving industrial heritage while serving a new cultural purpose.
- High Line (New York, USA): An elevated railway converted into a linear park, providing green space and recreational opportunities in a dense urban area.
Conclusion
The future of architecture will be defined by the integration of smart technologies and the sustainable practice of adaptive reuse. Smart cities will harness technology to create more efficient, livable, and sustainable urban environments, while adaptive reuse will preserve cultural heritage and reduce environmental impact. Together, these trends will shape a future where architecture not only meets the needs of modern society but also respects and enhances the built environment for generations to come.