Architecture and the Evolution of Healthcare Facilities
In recent decades, healthcare facilities have undergone significant transformations driven by advancements in medical technology, patient care models, and architectural design principles. This article explores how architecture has evolved to meet the evolving needs of healthcare environments, enhancing patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and overall well-being.
1. Early Hospital Designs
Historical overview of early hospital architecture focused on functionality and segregation of patients based on medical conditions.

2. The Shift towards Patient-Centered Care
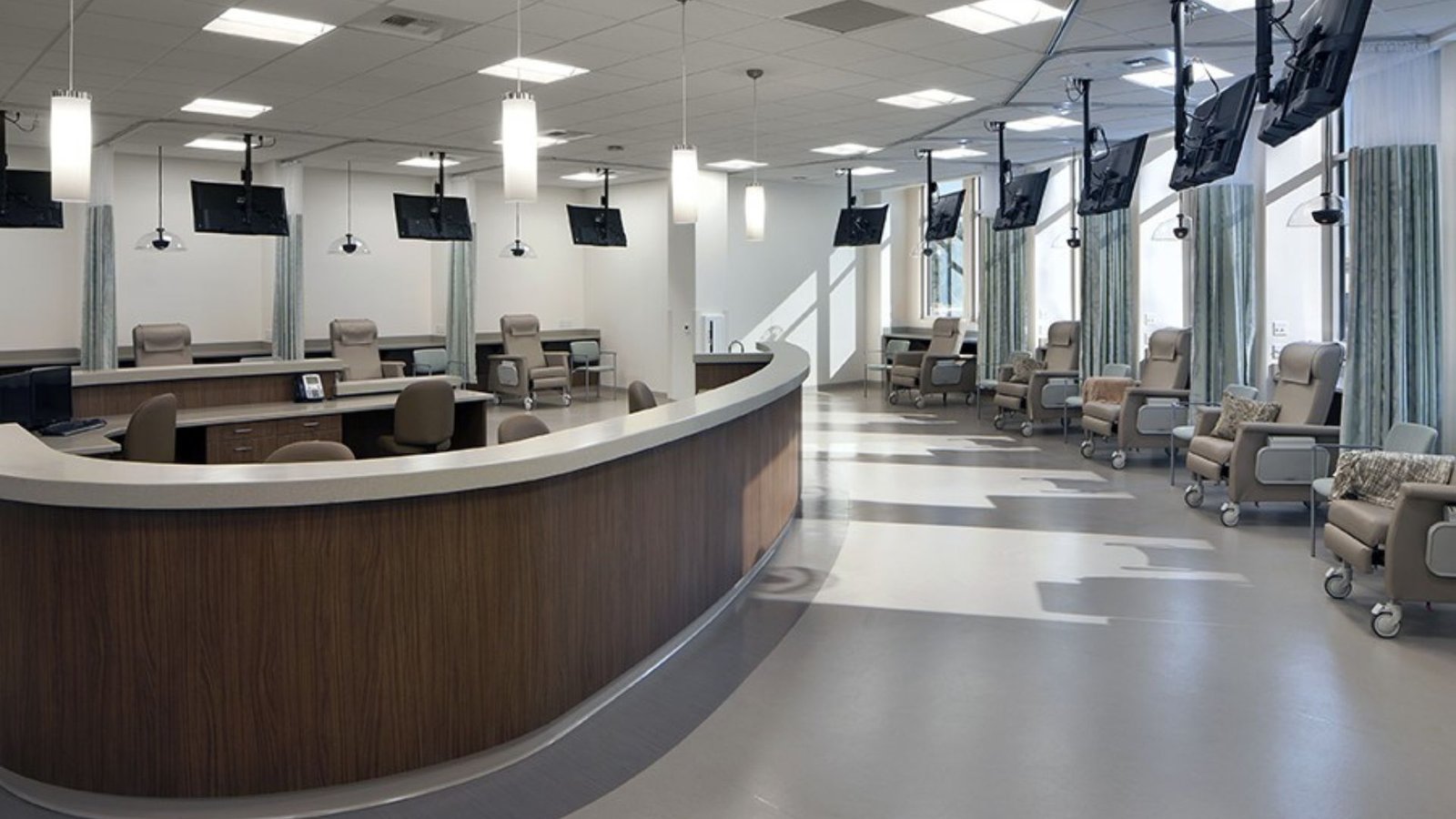
Transition to patient-centered care models influencing architectural layouts to prioritize patient comfort, privacy, and accessibility.
3. Evidence-Based Design (EBD)
Integration of EBD principles in healthcare architecture to improve clinical outcomes through research-driven design decisions.
4. Flexibility and Adaptability
Designing flexible spaces that can accommodate changes in healthcare delivery, technology advancements, and patient demographics.
5. Infection Control Measures
Implementation of architectural features and materials to reduce infection risks and improve overall hygiene.
6. Integration of Technology
Incorporation of advanced medical technologies into architectural design for seamless healthcare delivery and patient monitoring.
7. Sustainable Design Practices
Adoption of sustainable building materials and energy-efficient systems to minimize environmental impact and operational costs.
8. Wellness and Healing Environments
Creation of healing environments that promote patient well-being through natural light, green spaces, and calming aesthetics.
9. Accessibility Standards
Compliance with accessibility guidelines to ensure equitable access for patients with disabilities and elderly individuals.
10. Collaboration Spaces
Designing collaborative areas for healthcare teams to enhance communication, interdisciplinary care, and clinical efficiency.
11. Privacy Enhancements
Integration of soundproofing materials and spatial configurations to enhance patient confidentiality and comfort.
12. Resilience and Disaster Preparedness
Designing resilient healthcare facilities capable of withstanding natural disasters and ensuring continuity of care.
13. Cultural Sensitivity
Architectural designs that respect diverse cultural practices and preferences of patients and healthcare providers.
14. Research Facilities
Integration of research laboratories and innovation hubs within healthcare facilities to foster medical breakthroughs.
15. Mental Health Design Considerations
Incorporation of design elements that support mental health treatment and recovery processes.
16. Urban Health Centers
Designing healthcare facilities in urban settings to address population density, accessibility, and public health needs.
17. Telehealth Integration
Adapting architectural layouts to support telehealth services and virtual patient consultations.
18. Aging Population
Designing healthcare environments to cater to the growing elderly population’s specific needs and healthcare challenges.
19. Adaptive Reuse Projects
Transformation of existing buildings into healthcare facilities to meet community healthcare demands sustainably.
20. Patient and Staff Feedback
Incorporating feedback from patients and healthcare staff to continuously improve architectural designs and facility operations.
Conclusion
The evolution of healthcare architecture reflects broader societal shifts towards patient-centered care, sustainability, and technological integration. By embracing evidence-based design, sustainability practices, and innovative technologies, architects are redefining healthcare environments to support healing, well-being, and medical excellence. As healthcare needs continue to evolve, architecture will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of patient care and medical innovation.